
4. Chemical Reactions
Last Updated 8/26/2024, 22:25 MST)
Brown Chapter 3 Stoichiometry PowerPoint
Brown Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solution PowerPoint
4.1 Introduction for Reactions

4.2 Net Ionic Equations
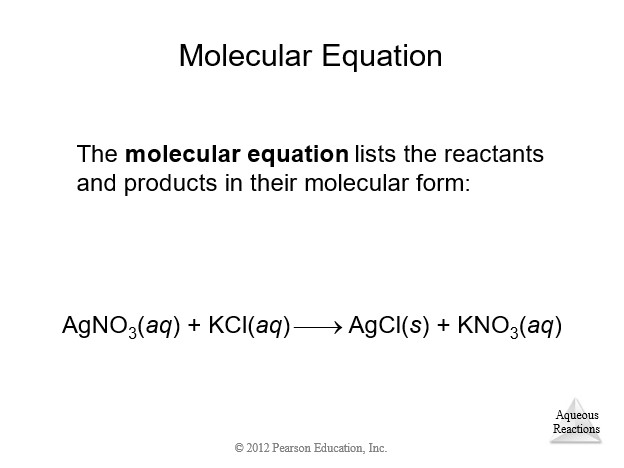

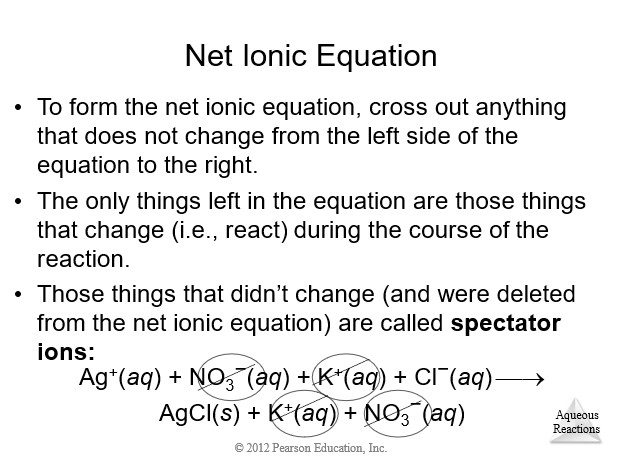

4.3 Representations of Reactions
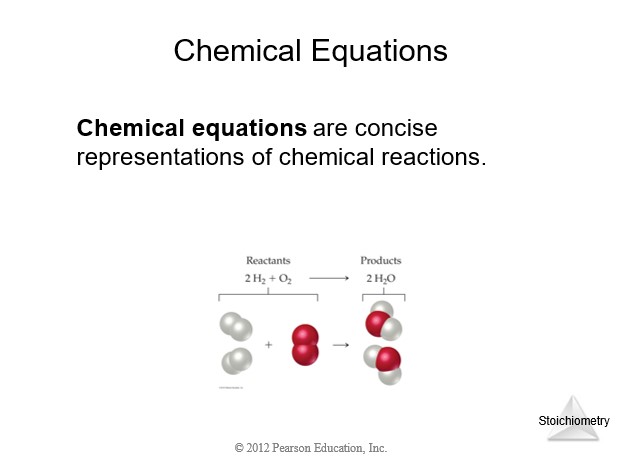
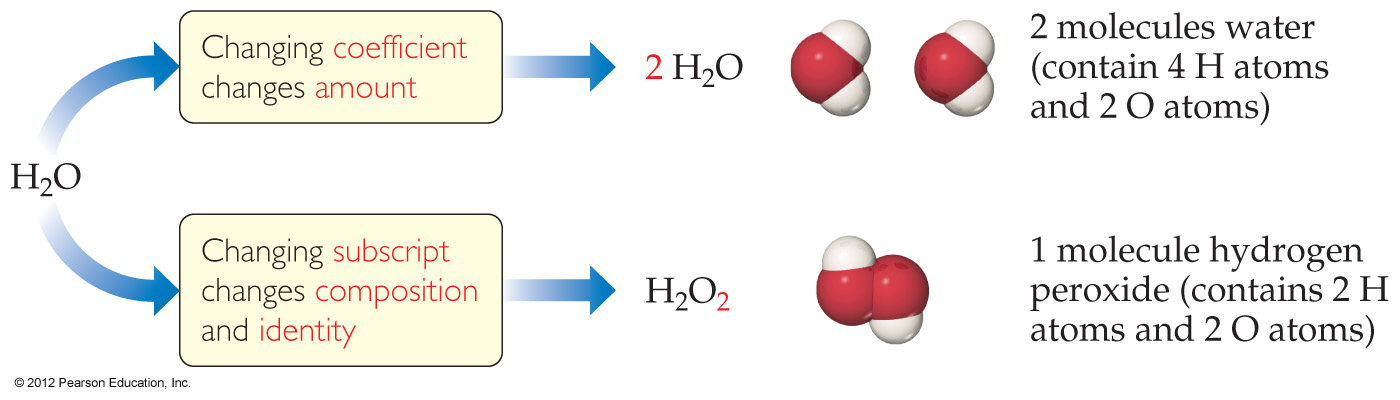
4.4 Physical and Chemical Changes

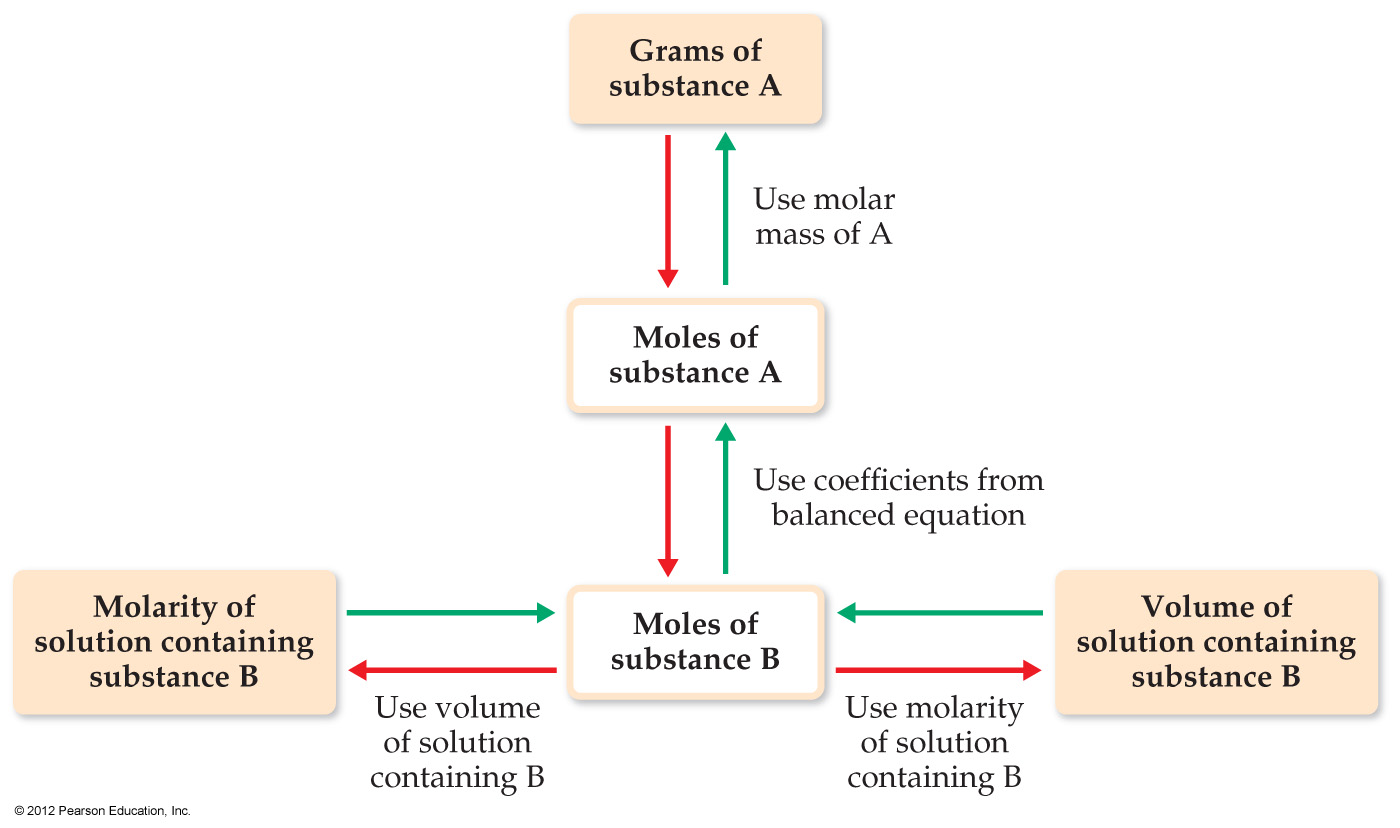
4.5 Stoichiometry
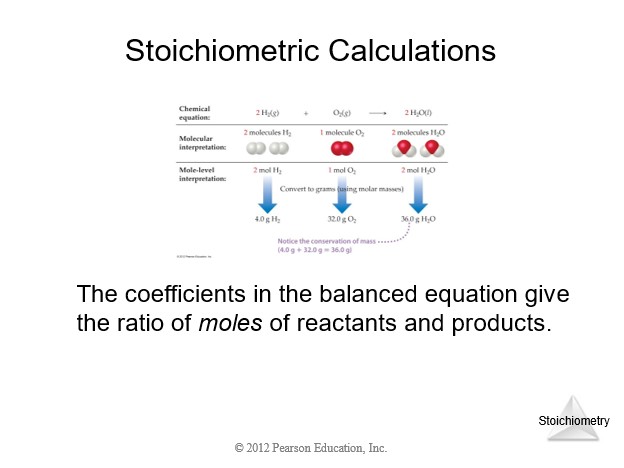
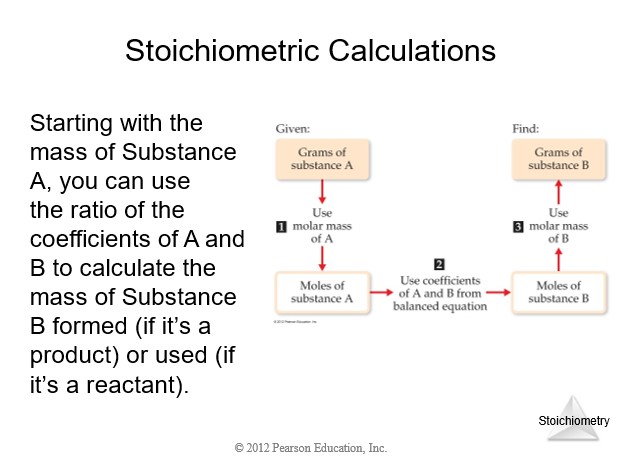
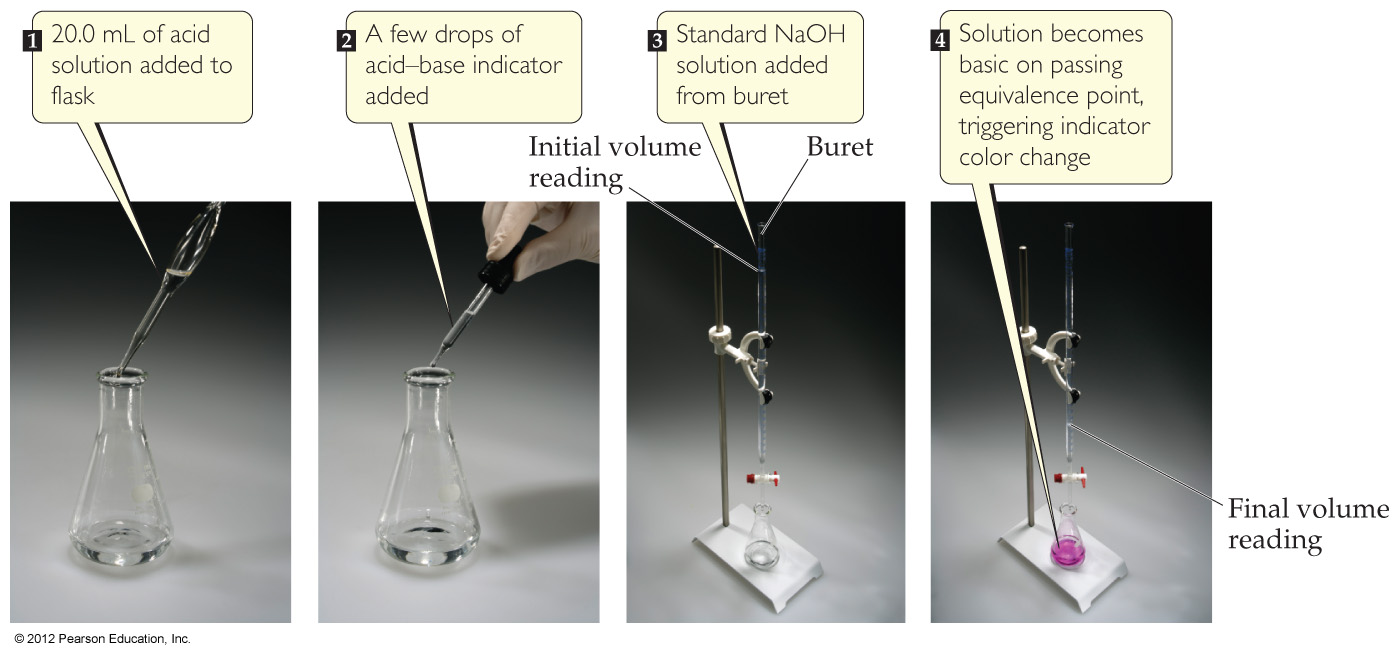
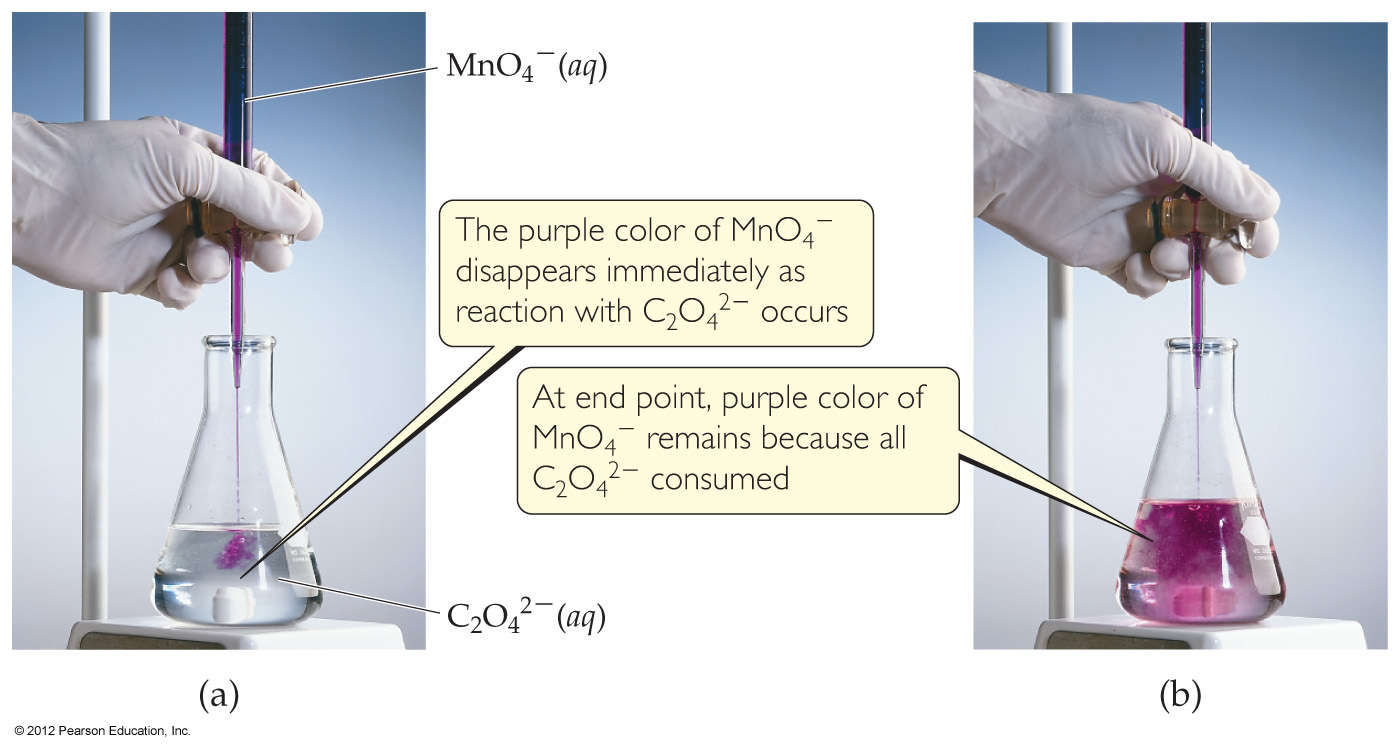
4.6 Introduction to Titration
4.7 Types of Chemical Reactions
| F2 > Cl2 > Br2 > I2 |
|---|
| 2HI + Br2 → 2HBr + I2 |
| 2HBr + Cl2 → 2HCl + Br2 |
| 2HCl + F2 → 2HF + Cl2 |
 reactions.jpg)
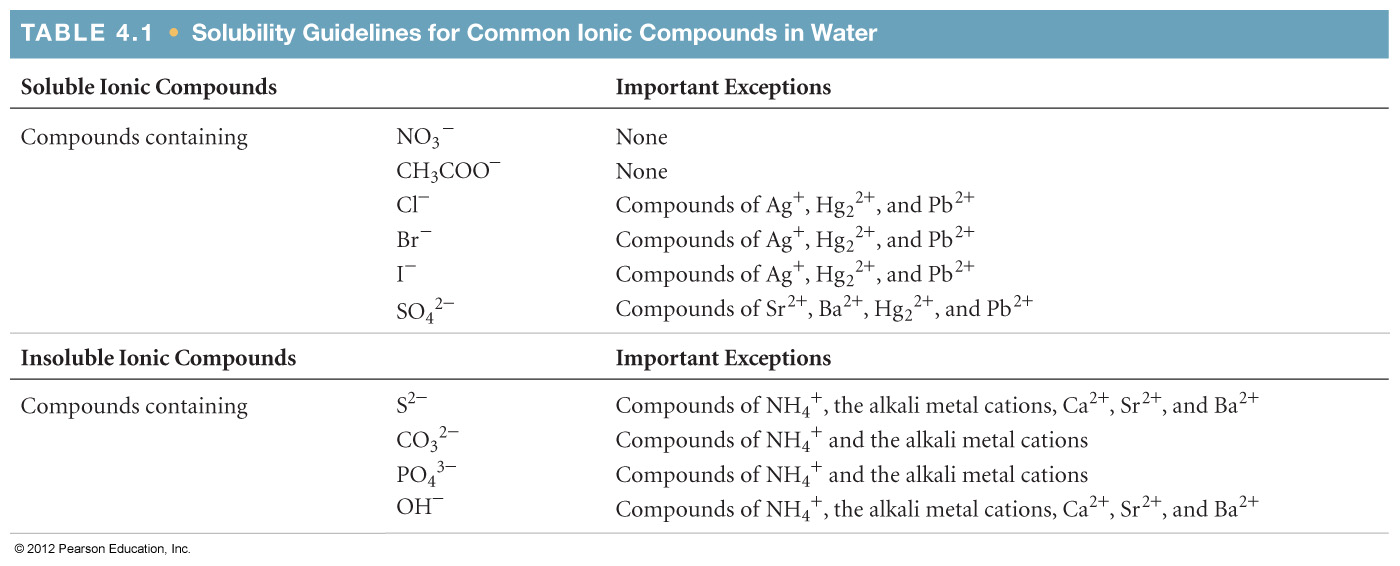
4.8 Introduction to Acid-Base Reactions
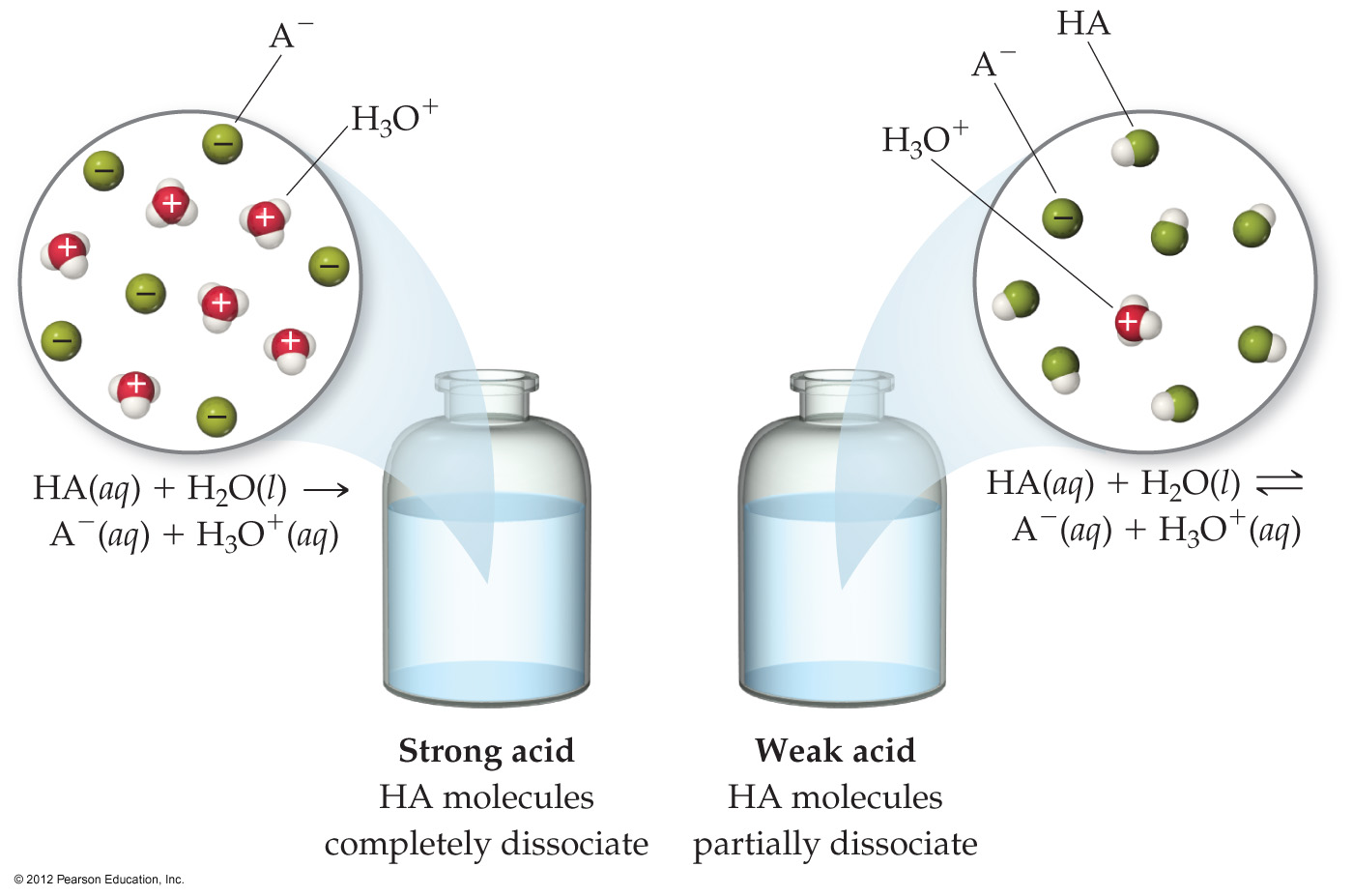
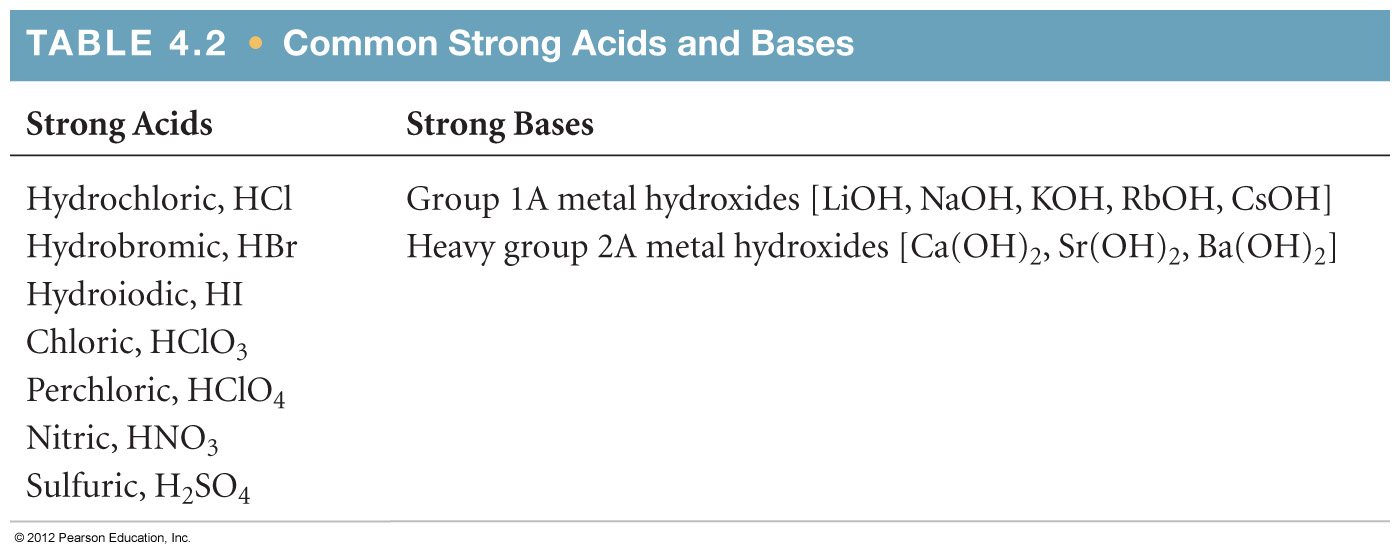
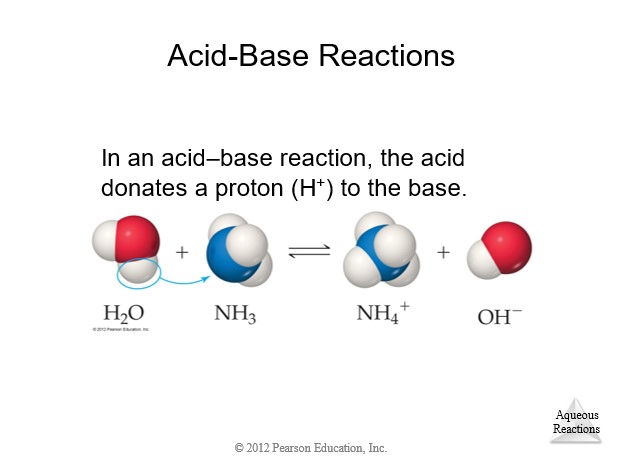


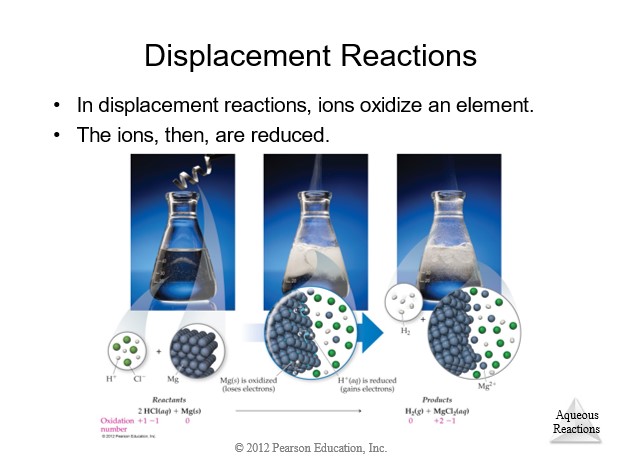
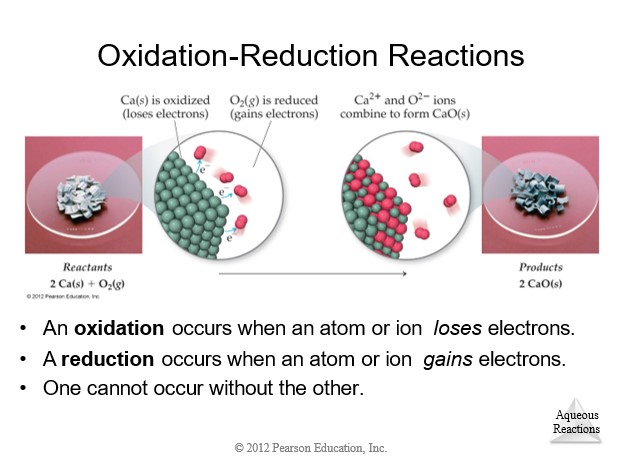
4.9 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
| Reaction Type | Redox? | Model | Guidelines |
| Synthesis/Combination | Maybe | A + B → C | - |
| Decomposition | Maybe | C → A + B | - |
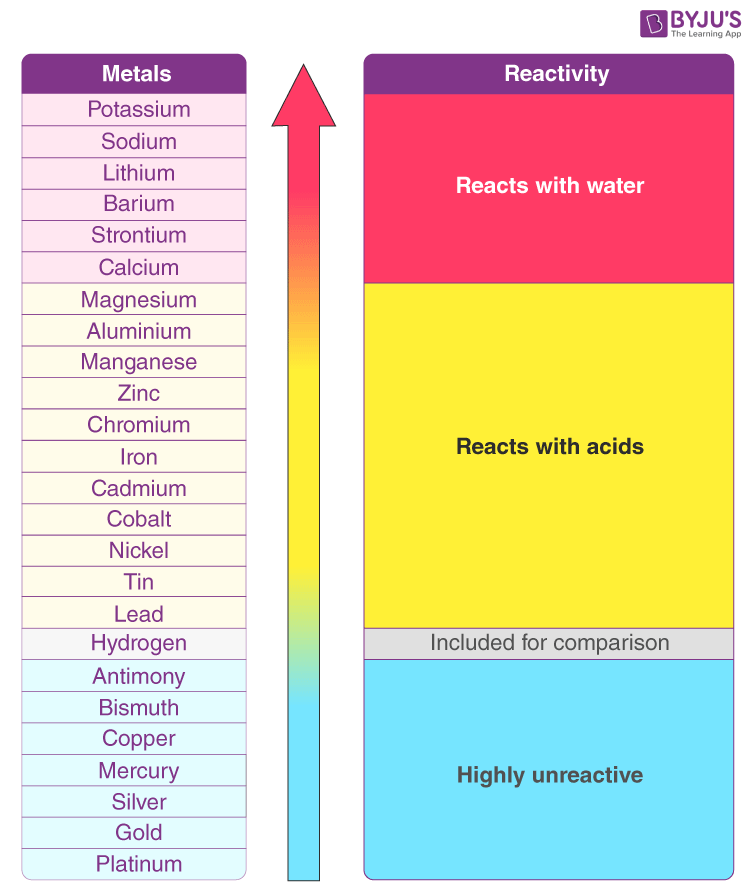
| Single Displacement | Always | AB + C → AC + B | Activity Series (metals or halogens) |
| Double Displacement (Metathesis/Exchange) | Never | AB + CD → AD + CB | Solubility Table or Acid-Base Strength |
| Combustion (Complete) | Always | CHO + O2 → CO2 + H2O | Principle reactant is any compound of C and H, and sometimes O. Products are always CO2 and H2O. |
| Combustion (Incomplete) | Always | CHO + O2 → CO + H2O | Products vary in an incomplete combustion reaction, but "half-way" is with CO and H2O products. |
Copyright© 2024 Chemical Solutions
bvins@mrvins.com